Lake Victoria on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Lake Victoria is one of the
Lake Victoria is one of the
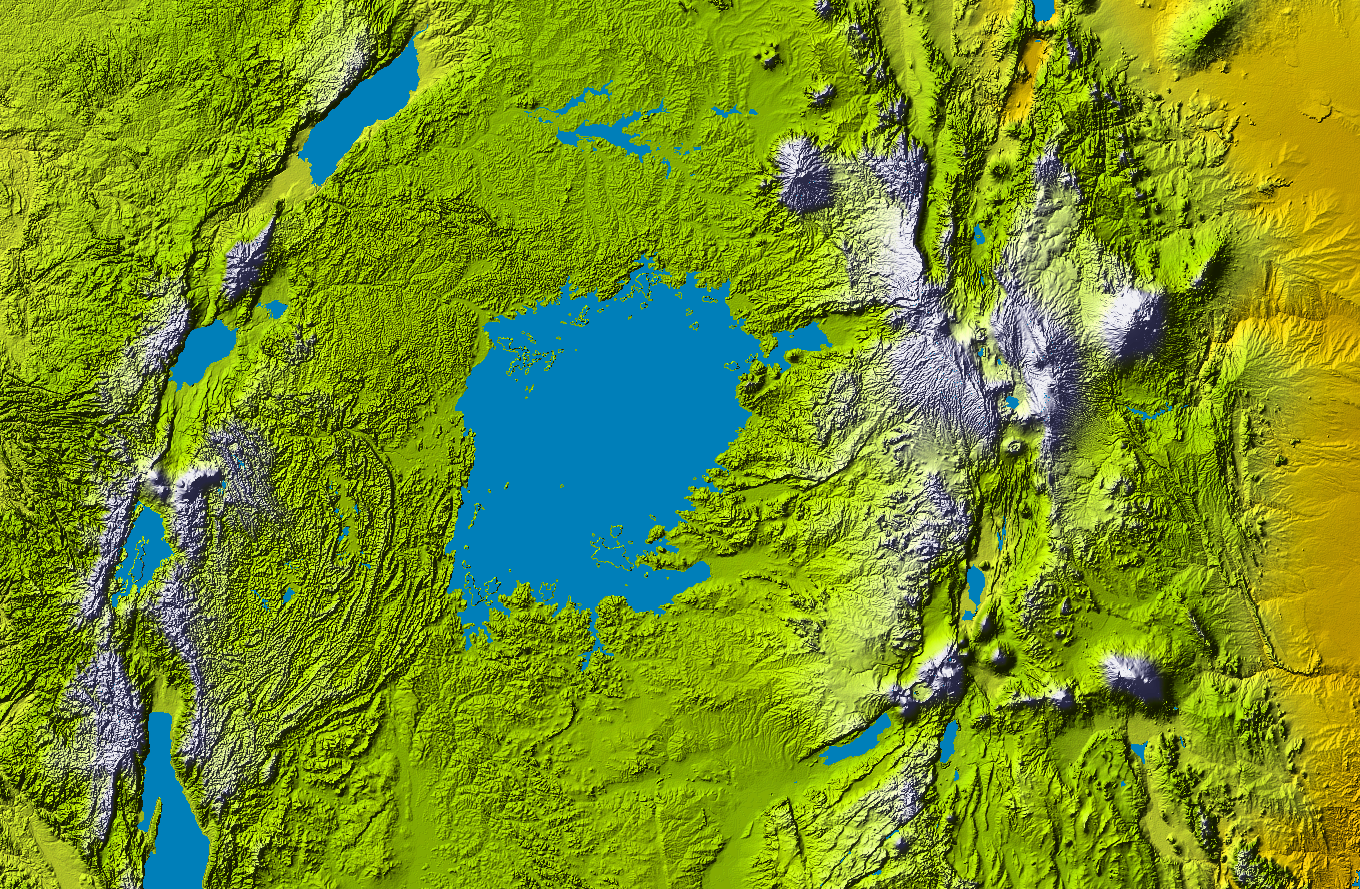 Geologically, Lake Victoria is relatively young at about 400,000 years old. It formed when westward-flowing rivers were dammed by an upthrown crustal block. During the
Geologically, Lake Victoria is relatively young at about 400,000 years old. It formed when westward-flowing rivers were dammed by an upthrown crustal block. During the
 The only outflow from Lake Victoria is the Nile River, which exits the lake near Jinja, Uganda. In terms of contributed water, this makes Lake Victoria the principal source of the longest branch of the Nile. However, the most distal source of the Nile Basin, and therefore the ultimate
The only outflow from Lake Victoria is the Nile River, which exits the lake near Jinja, Uganda. In terms of contributed water, this makes Lake Victoria the principal source of the longest branch of the Nile. However, the most distal source of the Nile Basin, and therefore the ultimate
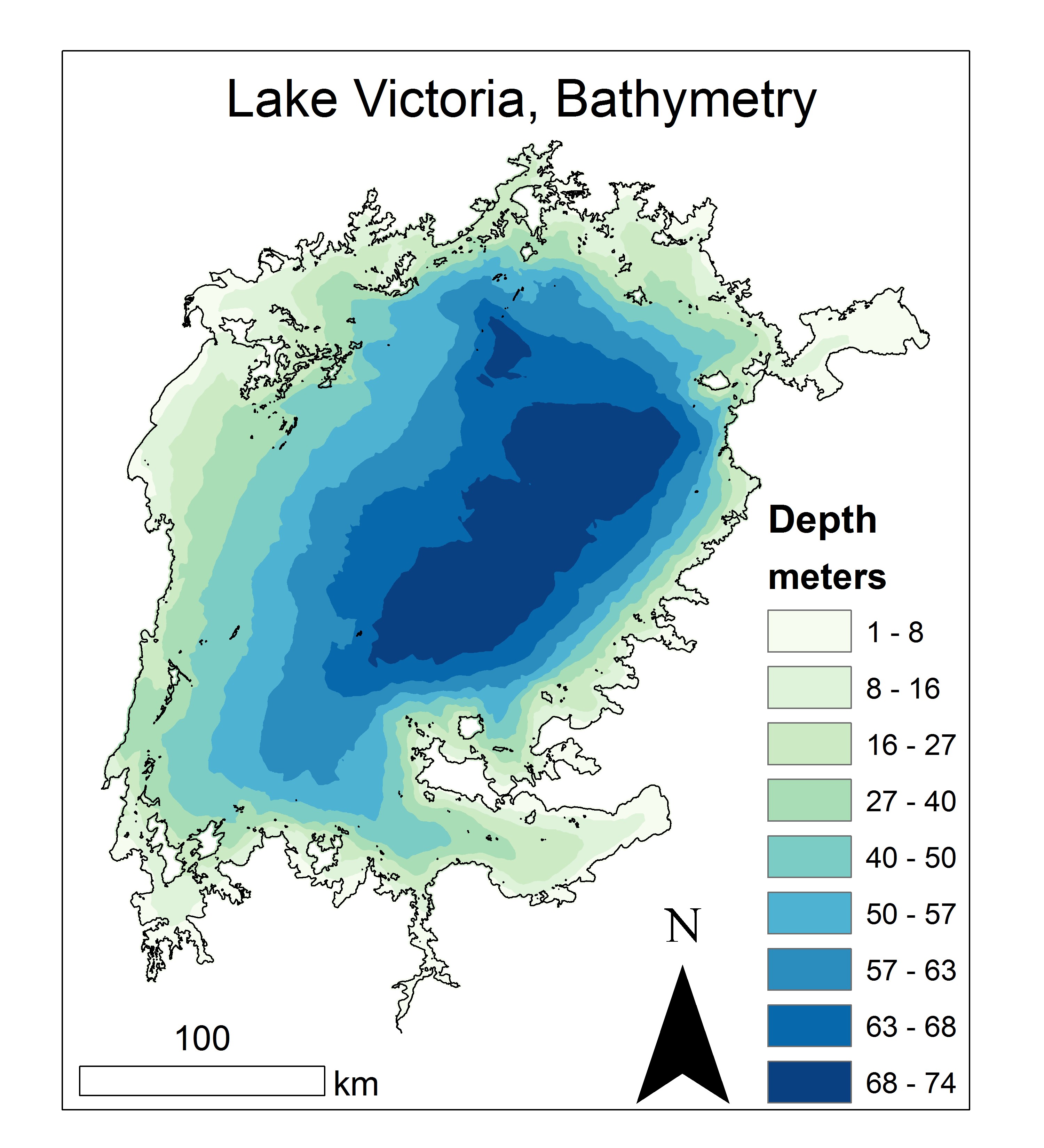 The lake is considered a shallow lake considering its large geographic area with a maximum depth of approximately and an average depth of . A 2016 project digitized ten-thousand points and created the first true bathymetric map of the lake. The deepest part of the lake is offset to the east of the lake near Kenya and the lake is generally shallower in the west along the Ugandan shoreline and the south along the Tanzanian shoreline.
The lake is considered a shallow lake considering its large geographic area with a maximum depth of approximately and an average depth of . A 2016 project digitized ten-thousand points and created the first true bathymetric map of the lake. The deepest part of the lake is offset to the east of the lake near Kenya and the lake is generally shallower in the west along the Ugandan shoreline and the south along the Tanzanian shoreline.
 Lake Victoria formerly was very rich in fish, including many endemics, but a high percentage of these became extinct since the 1940s. The main group in Lake Victoria is the haplochromine cichlids (''
Lake Victoria formerly was very rich in fish, including many endemics, but a high percentage of these became extinct since the 1940s. The main group in Lake Victoria is the haplochromine cichlids (''
Dark secret of the lake.
New Scientist. Retrieved 26 March 2017. and including an estimated 300 that still are undescribed.Sayer, C.A., L. Máiz-Tomé, and W.R.T. Darwall (2018). Freshwater biodiversity in the Lake Victoria Basin: Guidance for species conservation, site protection, The Victoria haplochromines are distinctly
The Victoria haplochromines are distinctly
Geographic Patterns
Eastern Africa. Retrieved 25 March 2017. Several of the remaining species are seriously threatened and additional extinctions are possible.Fiedler, P.L. and P M. Kareiva, editors (1998). Conservation Biology: For the Coming Decade. 2nd edition. pp. 209–10. Some species have survived in nearby small satellite lakes, have survived in refugias among rocks or
Fish Species in Victoria.
Retrieved 25 March 2017. At a genus level, most of these are widespread in Africa, but the very rare ''Xenobarbus'' and ''Xenoclarias'' are endemic to the lake, and the common ''Rastrineobola'' is near-endemic.
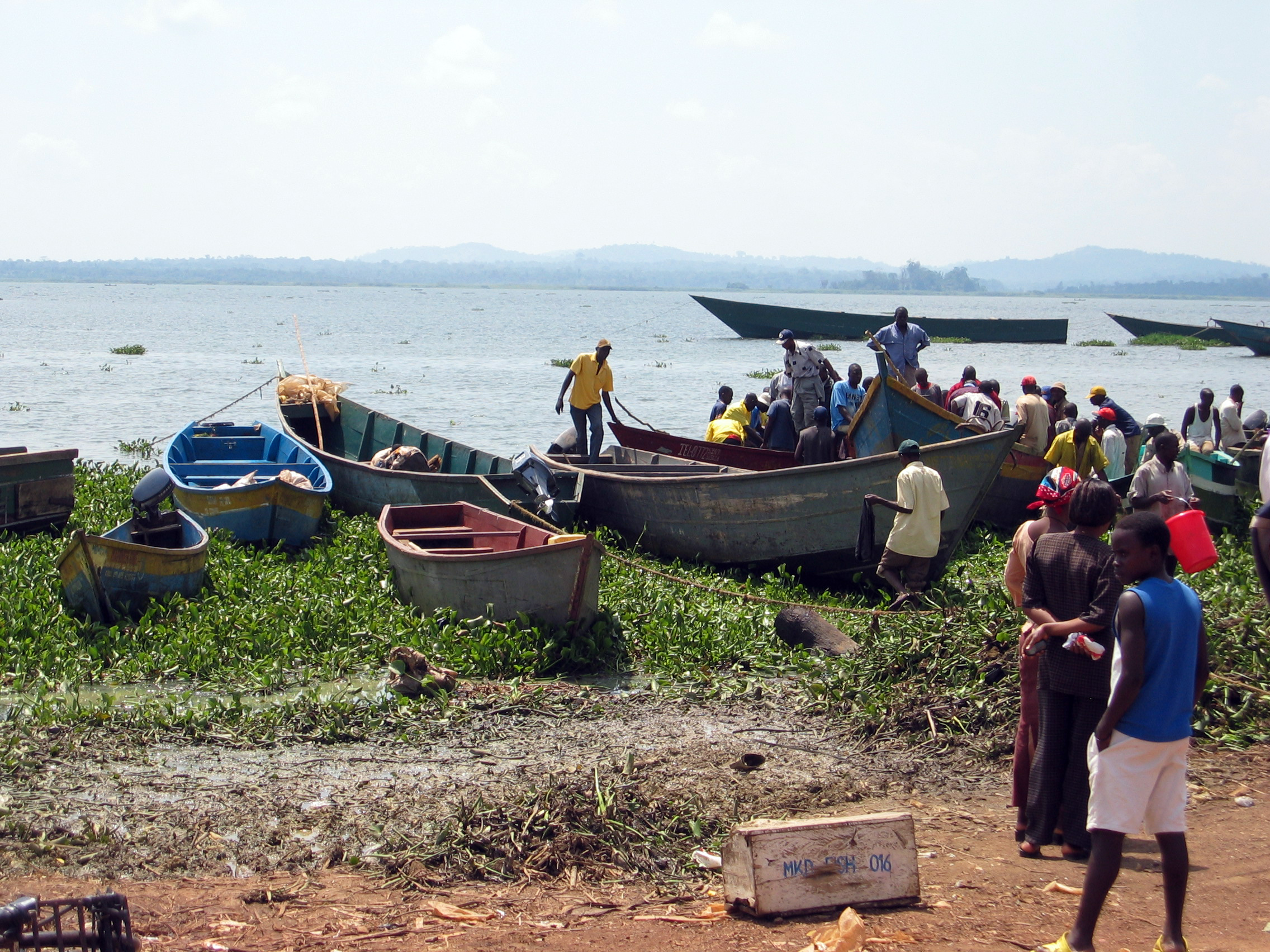 Lake Victoria supports Africa's largest inland fishery (as of 1997). Initially the fishery involved native species, especially tilapia and haplochromine cichlids, but also catfish (''Bagrus'', ''Clarias'', ''Synodontis'' and silver butter catfish), elephantfish, ningu (''Labeo victorianus'') and marbled lungfish (''Protopterus aethiopicus'').Lake Victoria Fisheries Organization (2016). Some of these, including tilapia and ningu (''Labeo victorianus''), had already declined in the first half of the 20th century due to overfishing. To boost fishing, several species of non-native tilapia and Nile perch were introduced to the lake in the 1950s. Nevertheless, the natives continued to dominate fisheries until the 1970s where their decline meant that there was a strong shift towards the non-native Nile tilapia (now 7 percent of catches), non-native Nile perch (60 percent) and the native Lake Victoria sardine (30 percent). Because of its small size, the abundant open-water Lake Victoria sardine only supported minor fisheries until the decline of other natives. At the peak in the early 1990s, of Nile perch were landed annually in Lake Victoria, but this has declined significantly in later years.
Lake Victoria supports Africa's largest inland fishery (as of 1997). Initially the fishery involved native species, especially tilapia and haplochromine cichlids, but also catfish (''Bagrus'', ''Clarias'', ''Synodontis'' and silver butter catfish), elephantfish, ningu (''Labeo victorianus'') and marbled lungfish (''Protopterus aethiopicus'').Lake Victoria Fisheries Organization (2016). Some of these, including tilapia and ningu (''Labeo victorianus''), had already declined in the first half of the 20th century due to overfishing. To boost fishing, several species of non-native tilapia and Nile perch were introduced to the lake in the 1950s. Nevertheless, the natives continued to dominate fisheries until the 1970s where their decline meant that there was a strong shift towards the non-native Nile tilapia (now 7 percent of catches), non-native Nile perch (60 percent) and the native Lake Victoria sardine (30 percent). Because of its small size, the abundant open-water Lake Victoria sardine only supported minor fisheries until the decline of other natives. At the peak in the early 1990s, of Nile perch were landed annually in Lake Victoria, but this has declined significantly in later years.
The Origins of the Nile Perch in Lake Victoria.
BioScience 55 (9): 780–787. Although these have contributed to the extinction of native fish by causing significant changes to the ecosystem, outcompeted natives and (in the case of the Nile tilapia) possibly hybridized with the highly threatened native tilapias, the most infamous introduction was the large and highly predatory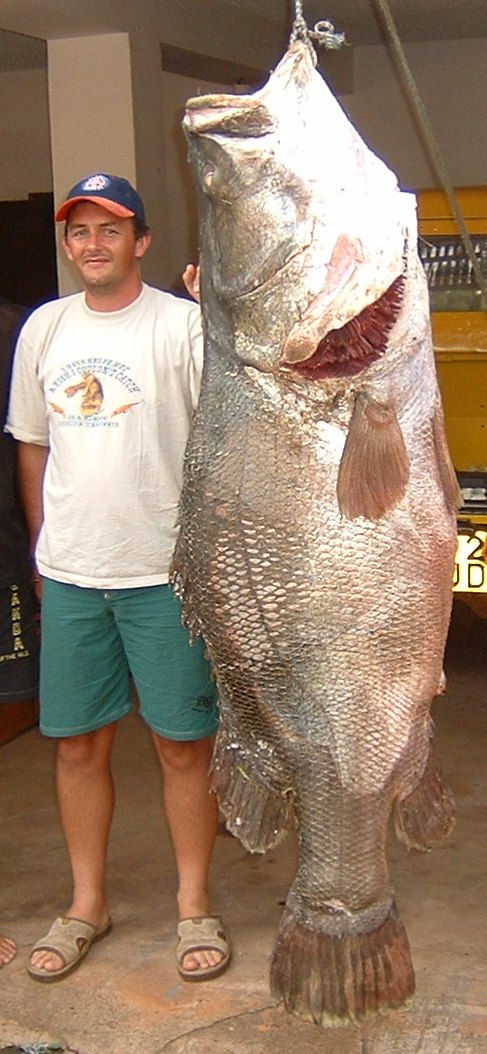 As early as the 1920s, it was proposed to introduce a large pelagic predator such as the Nile perch to improve the fisheries in the lake. At the same time it was warned that this could present a serious danger to the native fish species and required extensive research into possible ecological effects before done. These warnings primarily concerned the native tilapia ''O. esculentus'', as the smaller haplochromine cichlids (despite playing an important role in local fisheries) were regarded as "trash fish" by the colonial government. In the following decades, the pressure to introduce the Nile perch continued, as did warnings about the possible effects of doing it. The first introduction of Nile perch to the region, done by the Uganda Game and Fisheries Department (then part of the colonial government) and local African fish guards, happened upstream of Murchison Falls directly after the completion of the Owen Falls Dam in 1954. This allowed it to spread to Lake Kyoga where additional Nile perch were released in 1955, but not Victoria itself. Scientists argued that further introduction should wait until research showed the effect of the introduction in Kyoga, but by the late 1950s, Nile perch began being caught in Lake Victoria. As the species was already present, there were few objections when more Nile perch were transferred to Victoria to further bolster the stock in 1962–63.
The origin of the first Victoria introductions in the 1950s is not entirely clear and indisputable evidence is lacking. Uganda Game and Fisheries Department (UGFD) officials denied that they were involved, but circumstantial evidence suggests otherwise and local Africans employed by UGFD have said that they introduced the species in 1954–55 under the directive of senior officials. UGFD officials argued that Nile perch must have spread to Lake Victoria by themselves by passing through the Owen Falls Dam when shut down for maintenance, but this is considered highly unlikely by many scientists. The Nile perch had spread throughout the lake by 1970. Initially the population of the Nile perch was relatively low, but a drastic increase happened, peaking in the 1980s, followed by a decline starting in the 1990s.
Due to the presence of the Nile perch, the natural balance of the lake's ecosystem has been disrupted. The food chain is being altered and in some cases, broken by the indiscriminate eating habits of the Nile perch.
The subsequent decrease in the number of algae-eating fish allows the algae to grow at an alarming rate, thereby choking the lake. The increasing amounts of algae, in turn, increase the amount of detritus (dead plant material) that falls to the deeper portions of the lake before decomposing. As a by-product of this the oxygen levels in the deeper layer of water are being depleted. Without oxygen, any aerobic life (such as fish) cannot exist in the deeper parts of the lake, forcing all life to exist within a narrow range of depth. In this way, the Nile perch has degraded the diverse and thriving ecosystem that was once Lake Victoria. The abundance of aquatic life is not the only dependent of the lake: more than thirty million people in Tanzania, Kenya and Uganda rely on the lake for its natural resources.
Hundreds of endemic species that evolved under the special conditions offered by the protection of Lake Victoria have been lost due to extinction, and several more are still threatened. Their loss is devastating for the lake, the fields of ecology, genetics and evolution biology, and more evidently, for the local fisheries. Local fisheries once depended on catching the lungfish, tilapia, carp and catfish that comprise the local diet.
Today, the composition and yields of such fish catches are virtually negligible. Extensive fish kills, Nile perch, loss of habitat and overfishing have caused many fisheries to collapse and many protein sources to be unavailable at the market for local consumption. Few fisheries, though, have been able to make the switch to catching the Nile perch, since that requires a significant amount of capital resources.
As early as the 1920s, it was proposed to introduce a large pelagic predator such as the Nile perch to improve the fisheries in the lake. At the same time it was warned that this could present a serious danger to the native fish species and required extensive research into possible ecological effects before done. These warnings primarily concerned the native tilapia ''O. esculentus'', as the smaller haplochromine cichlids (despite playing an important role in local fisheries) were regarded as "trash fish" by the colonial government. In the following decades, the pressure to introduce the Nile perch continued, as did warnings about the possible effects of doing it. The first introduction of Nile perch to the region, done by the Uganda Game and Fisheries Department (then part of the colonial government) and local African fish guards, happened upstream of Murchison Falls directly after the completion of the Owen Falls Dam in 1954. This allowed it to spread to Lake Kyoga where additional Nile perch were released in 1955, but not Victoria itself. Scientists argued that further introduction should wait until research showed the effect of the introduction in Kyoga, but by the late 1950s, Nile perch began being caught in Lake Victoria. As the species was already present, there were few objections when more Nile perch were transferred to Victoria to further bolster the stock in 1962–63.
The origin of the first Victoria introductions in the 1950s is not entirely clear and indisputable evidence is lacking. Uganda Game and Fisheries Department (UGFD) officials denied that they were involved, but circumstantial evidence suggests otherwise and local Africans employed by UGFD have said that they introduced the species in 1954–55 under the directive of senior officials. UGFD officials argued that Nile perch must have spread to Lake Victoria by themselves by passing through the Owen Falls Dam when shut down for maintenance, but this is considered highly unlikely by many scientists. The Nile perch had spread throughout the lake by 1970. Initially the population of the Nile perch was relatively low, but a drastic increase happened, peaking in the 1980s, followed by a decline starting in the 1990s.
Due to the presence of the Nile perch, the natural balance of the lake's ecosystem has been disrupted. The food chain is being altered and in some cases, broken by the indiscriminate eating habits of the Nile perch.
The subsequent decrease in the number of algae-eating fish allows the algae to grow at an alarming rate, thereby choking the lake. The increasing amounts of algae, in turn, increase the amount of detritus (dead plant material) that falls to the deeper portions of the lake before decomposing. As a by-product of this the oxygen levels in the deeper layer of water are being depleted. Without oxygen, any aerobic life (such as fish) cannot exist in the deeper parts of the lake, forcing all life to exist within a narrow range of depth. In this way, the Nile perch has degraded the diverse and thriving ecosystem that was once Lake Victoria. The abundance of aquatic life is not the only dependent of the lake: more than thirty million people in Tanzania, Kenya and Uganda rely on the lake for its natural resources.
Hundreds of endemic species that evolved under the special conditions offered by the protection of Lake Victoria have been lost due to extinction, and several more are still threatened. Their loss is devastating for the lake, the fields of ecology, genetics and evolution biology, and more evidently, for the local fisheries. Local fisheries once depended on catching the lungfish, tilapia, carp and catfish that comprise the local diet.
Today, the composition and yields of such fish catches are virtually negligible. Extensive fish kills, Nile perch, loss of habitat and overfishing have caused many fisheries to collapse and many protein sources to be unavailable at the market for local consumption. Few fisheries, though, have been able to make the switch to catching the Nile perch, since that requires a significant amount of capital resources.
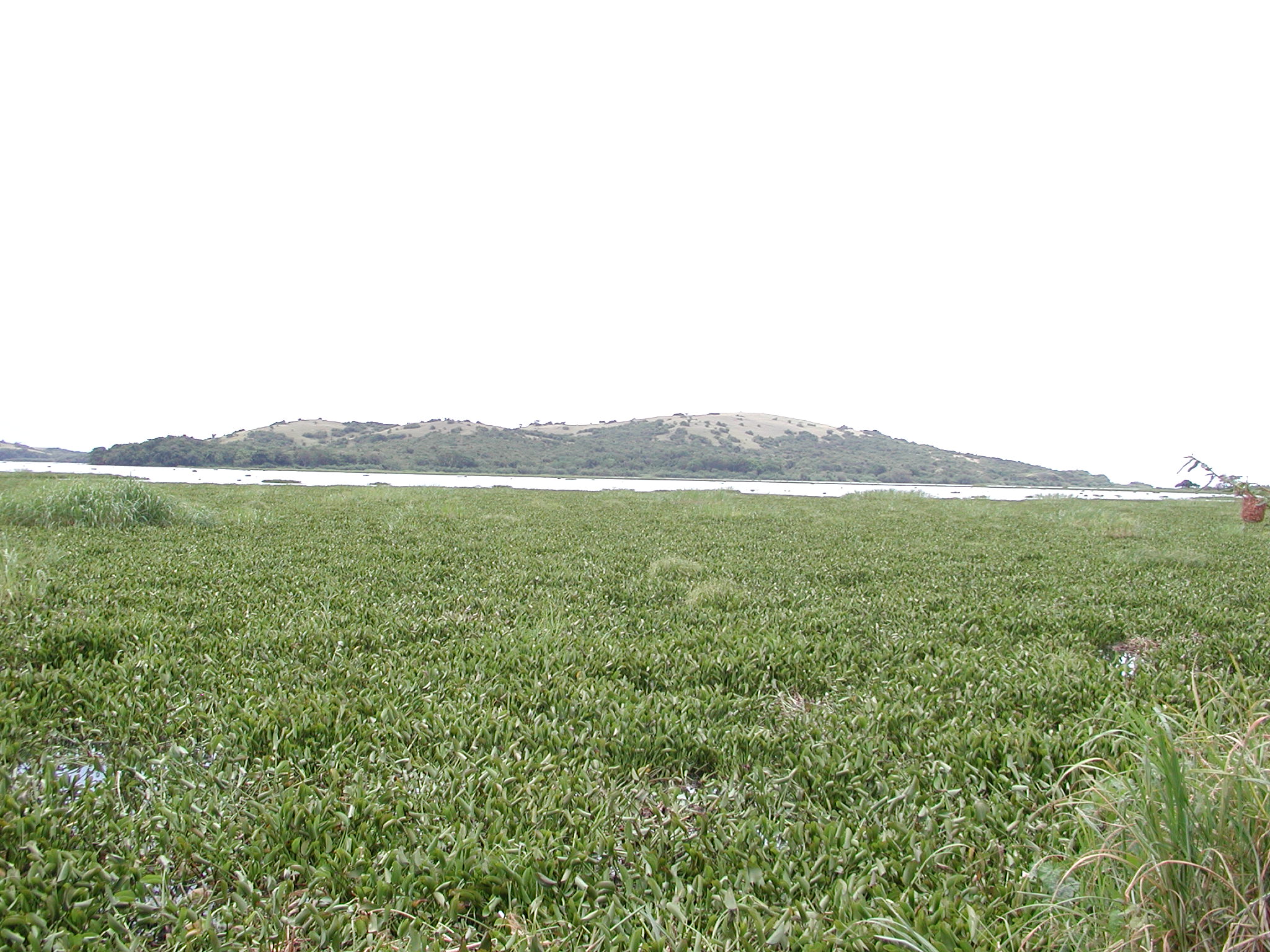 The water hyacinth has become a major invasive plant species in Lake Victoria.
The release of large amounts of untreated wastewater (sewage) and agricultural and industrial runoff directly into Lake Victoria over the past 30 years has greatly increased the nutrient levels of nitrogen and phosphorus in the lake "triggering massive growth of exotic water hyacinth, which colonised the lake in the late 1990s".Luilo, G.B. (August 01, 2008). Lake Victoria water resources management challenges and prospects: a need for equitable and sustainable institutional and regulatory frameworks ''African Journal of Aquatic Science'' 33, 2, 105–13. This invasive weed creates anoxic (total depletion of oxygen levels) conditions in the lake inhibiting decomposing plant material, raising toxicity and disease levels to both fish and people. At the same time, the plant's mat or "web" creates a barrier for boats and ferries to maneuver, impedes access to the shoreline, interferes with hydroelectric power generation, and blocks the intake of water for industries.Kateregga, E., & Sterner, T. (January 01, 2009). "Lake Victoria Fish Stocks and the Effects of Water Hyacinth". ''Journal of Environment & Development'', 18, 1, 62–78.Albright, T.P., Moorhouse, T.G., & McNabb, T.J. (January 1, 2004). "The Rise and Fall of Water Hyacinth in Lake Victoria and the Kagera River Basin, 1989-2001". ''Journal of Aquatic Plant Management'', 42, 73–84. On the other hand, water hyacinth mats can potentially have a positive effect on fish life in that they create a barrier to overfishing and allow for fish growth, there has even been the reappearance of some fish species thought to have been extinct in recent years. The overall effects of the water hyacinth, however, are still unknown.
Growth of the water hyacinth in Lake Victoria has been tracked since 1993, reaching its maxima biomass in 1997 and then declining again by the end of 2001. Greater growth was observed in the northern part of the lake, in relatively protected areas, which may be linked to current and weather patterns and could also be due to the climate and water conditions, which are more suitable to the plants growth (as there are large urban areas to the north end of the lake, in Uganda). The invasive weed was first attempted to be controlled by hand, removed manually from the lake; however, re-growth occurred quickly. Public awareness exercises were also conducted. More recently, measures have been used such as the introduction of natural insect predators, including two different water hyacinth weevils and large harvesting and chopping boats, which seem to be much more effective in eliminating the water hyacinth. A green power plant that uses harvested water hyacinth (but also can use other degradable waste) was constructed in Kisumu County in 2013. In addition to the biogas it produces, its by-product can be used as fertilizer.
Other factors which may have contributed to the decline of the water hyacinth in Lake Victoria include varying weather patterns, such as El Niño during the last few months of 1997 and first six months of 1998 bringing with it higher levels of water in the lake and thus dislodging the plants. Heavy winds and rains along with their subsequent waves may have also damaged the plants during this same time frame. The plants may not have been destroyed, instead merely moved to another location. Additionally, the water quality, nutrient supply, temperature, and other environmental factors could have played a role. Overall, the timing of the decline could be linked to all of these factors and perhaps together, in combination, they were more effective than any one deterrent would have been by itself. The water hyacinth is in remission and this trend could be permanent if control efforts are continued.
The water hyacinth has become a major invasive plant species in Lake Victoria.
The release of large amounts of untreated wastewater (sewage) and agricultural and industrial runoff directly into Lake Victoria over the past 30 years has greatly increased the nutrient levels of nitrogen and phosphorus in the lake "triggering massive growth of exotic water hyacinth, which colonised the lake in the late 1990s".Luilo, G.B. (August 01, 2008). Lake Victoria water resources management challenges and prospects: a need for equitable and sustainable institutional and regulatory frameworks ''African Journal of Aquatic Science'' 33, 2, 105–13. This invasive weed creates anoxic (total depletion of oxygen levels) conditions in the lake inhibiting decomposing plant material, raising toxicity and disease levels to both fish and people. At the same time, the plant's mat or "web" creates a barrier for boats and ferries to maneuver, impedes access to the shoreline, interferes with hydroelectric power generation, and blocks the intake of water for industries.Kateregga, E., & Sterner, T. (January 01, 2009). "Lake Victoria Fish Stocks and the Effects of Water Hyacinth". ''Journal of Environment & Development'', 18, 1, 62–78.Albright, T.P., Moorhouse, T.G., & McNabb, T.J. (January 1, 2004). "The Rise and Fall of Water Hyacinth in Lake Victoria and the Kagera River Basin, 1989-2001". ''Journal of Aquatic Plant Management'', 42, 73–84. On the other hand, water hyacinth mats can potentially have a positive effect on fish life in that they create a barrier to overfishing and allow for fish growth, there has even been the reappearance of some fish species thought to have been extinct in recent years. The overall effects of the water hyacinth, however, are still unknown.
Growth of the water hyacinth in Lake Victoria has been tracked since 1993, reaching its maxima biomass in 1997 and then declining again by the end of 2001. Greater growth was observed in the northern part of the lake, in relatively protected areas, which may be linked to current and weather patterns and could also be due to the climate and water conditions, which are more suitable to the plants growth (as there are large urban areas to the north end of the lake, in Uganda). The invasive weed was first attempted to be controlled by hand, removed manually from the lake; however, re-growth occurred quickly. Public awareness exercises were also conducted. More recently, measures have been used such as the introduction of natural insect predators, including two different water hyacinth weevils and large harvesting and chopping boats, which seem to be much more effective in eliminating the water hyacinth. A green power plant that uses harvested water hyacinth (but also can use other degradable waste) was constructed in Kisumu County in 2013. In addition to the biogas it produces, its by-product can be used as fertilizer.
Other factors which may have contributed to the decline of the water hyacinth in Lake Victoria include varying weather patterns, such as El Niño during the last few months of 1997 and first six months of 1998 bringing with it higher levels of water in the lake and thus dislodging the plants. Heavy winds and rains along with their subsequent waves may have also damaged the plants during this same time frame. The plants may not have been destroyed, instead merely moved to another location. Additionally, the water quality, nutrient supply, temperature, and other environmental factors could have played a role. Overall, the timing of the decline could be linked to all of these factors and perhaps together, in combination, they were more effective than any one deterrent would have been by itself. The water hyacinth is in remission and this trend could be permanent if control efforts are continued.
 Pollution of Lake Victoria is mainly due to discharge of raw sewage into the lake, dumping of domestic and industrial waste, and fertiliser and chemicals from farms.
The Lake Victoria basin, while generally rural, has many major centres of population. Its shores are dotted with key cities and towns, including Kisumu, Kisii, Kenya, Kisii, and Homa Bay in Kenya; Kampala, Jinja, Uganda, Jinja and Entebbe in Uganda; and Bukoba, Mwanza, and Musoma in Tanzania. These cities and towns are also home to many factories that discharge some chemicals directly into the lake or its influent rivers. The set up of small beaches and local authorities around the lake lack proper sewage treatment facilities allowing pollutants to find their way into the water. Large parts of these urban areas also discharge untreated (raw) sewage into the river, increasing its
Pollution of Lake Victoria is mainly due to discharge of raw sewage into the lake, dumping of domestic and industrial waste, and fertiliser and chemicals from farms.
The Lake Victoria basin, while generally rural, has many major centres of population. Its shores are dotted with key cities and towns, including Kisumu, Kisii, Kenya, Kisii, and Homa Bay in Kenya; Kampala, Jinja, Uganda, Jinja and Entebbe in Uganda; and Bukoba, Mwanza, and Musoma in Tanzania. These cities and towns are also home to many factories that discharge some chemicals directly into the lake or its influent rivers. The set up of small beaches and local authorities around the lake lack proper sewage treatment facilities allowing pollutants to find their way into the water. Large parts of these urban areas also discharge untreated (raw) sewage into the river, increasing its
 The first recorded information about Lake Victoria comes from Arab traders plying the inland routes in search of gold, ivory, other precious commodities, and slaves.
The first recorded information about Lake Victoria comes from Arab traders plying the inland routes in search of gold, ivory, other precious commodities, and slaves.
 The lake existed and was known to many Africans in the catchment area long before it was sighted by a European ethnic groups, European in 1858 when the British people, British List of explorers, explorer
The lake existed and was known to many Africans in the catchment area long before it was sighted by a European ethnic groups, European in 1858 when the British people, British List of explorers, explorer
 The only outflow for Lake Victoria is at Jinja, Uganda, where it forms the Victoria Nile. The water for at least 12,000 years has drained across a natural rock weir. In 1952, engineers acting for the government of British Uganda, Colonial Uganda blasted out the weir and reservoir to replace it with an artificial barrage to control the level of the lake and reduce the gradual erosion of the rock weir. A standard for mimicking the old rate of outflow called the "agreed curve" was established, setting the maximum flow rate at 300 to 1,700 Cubic metre per second, cubic metres per second (392–2,224 cubic yard, cu yd/sec) depending on the lake's water level.
In 2002, Uganda completed a second hydroelectric complex in the area, the Kiira Hydroelectric Power Station, with World Bank assistance. By 2006, the water levels in Lake Victoria had reached an 80-year low, and Daniel Kull, an independent hydrologist living in Nairobi, Kenya, calculated that Uganda was releasing about twice as much water as is allowed under the agreement, and was primarily responsible for recent drops in the lake's level.
The only outflow for Lake Victoria is at Jinja, Uganda, where it forms the Victoria Nile. The water for at least 12,000 years has drained across a natural rock weir. In 1952, engineers acting for the government of British Uganda, Colonial Uganda blasted out the weir and reservoir to replace it with an artificial barrage to control the level of the lake and reduce the gradual erosion of the rock weir. A standard for mimicking the old rate of outflow called the "agreed curve" was established, setting the maximum flow rate at 300 to 1,700 Cubic metre per second, cubic metres per second (392–2,224 cubic yard, cu yd/sec) depending on the lake's water level.
In 2002, Uganda completed a second hydroelectric complex in the area, the Kiira Hydroelectric Power Station, with World Bank assistance. By 2006, the water levels in Lake Victoria had reached an 80-year low, and Daniel Kull, an independent hydrologist living in Nairobi, Kenya, calculated that Uganda was releasing about twice as much water as is allowed under the agreement, and was primarily responsible for recent drops in the lake's level.
Decreasing levels of Lake Victoria Worry East African Countries
New Scientist article
on Uganda's violation of the agreed curve for hydroelectric water flow.
Dams Draining Lake Victoria
''A Naturalist on Lake Victoria, with an Account of Sleeping Sickness and the Tse-tse Fly''
(1920). T.F. Unwin Ltd, London; Biodiversity Archive
Video of Lake Victoria
* Institutions of the East African Community
Lake Victoria Fisheries Organisation
{{DEFAULTSORT:Victoria Lake Victoria, African Great Lakes Lakes of Kenya Lakes of Tanzania Lakes of Uganda Geography of Kampala Nile Kenya–Uganda border Kenya–Tanzania border Tanzania–Uganda border International lakes of Africa Border tripoints Geography of Kagera Region Geography of Mwanza Region Geography of Mara Region Kisumu County Homa Bay County
 Lake Victoria is one of the
Lake Victoria is one of the African Great Lakes
The African Great Lakes ( sw, Maziwa Makuu; rw, Ibiyaga bigari) are a series of lakes constituting the part of the Rift Valley lakes in and around the East African Rift. They include Lake Victoria, the second-largest fresh water lake in th ...
. With a surface area of approximately , Lake Victoria is Africa's largest lake by area, the world's largest tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
lake, and the world's second-largest fresh water lake by surface area after Lake Superior
Lake Superior in central North America is the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface areaThe Caspian Sea is the largest lake, but is saline, not freshwater. and the third-largest by volume, holding 10% of the world's surface fresh wa ...
in North America. In terms of volume, Lake Victoria is the world's ninth-largest continental lake, containing about of water. Lake Victoria occupies a shallow depression in Africa. The lake has an average depth of and a maximum depth of .United Nations, ''Development and Harmonisation of Environmental Laws Volume 1: Report on the Legal and Institutional Issues in the Lake Victoria Basin'', United Nations, 1999, page 17 Its catchment area
In human geography, a catchment area is the area from which a location, such as a city, service or institution, attracts a population that uses its services and economic opportunities. Catchment areas may be defined based on from where people are ...
covers . The lake has a shoreline of when digitized at the 1:25,000 level, with islands constituting 3.7% of this length.
The lake's area is divided among three countries: Kenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
...
occupies 6% (), Uganda
}), is a landlocked country in East Africa. The country is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the south by Tanzania. The sou ...
45% (), and Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
49% ().
Though having multiple local language names ( luo, Nam Lolwe; lg, 'Nnalubaale; rw, Nyanza; also ''Ukerewe''), the lake was renamed after Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days was longer than that of any previo ...
by the explorer John Hanning Speke
Captain John Hanning Speke (4 May 1827 – 15 September 1864) was an English explorer and officer in the British Indian Army who made three exploratory expeditions to Africa. He is most associated with the search for the source of the Nil ...
, the first Briton
British people or Britons, also known colloquially as Brits, are the citizens of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, the British Overseas Territories, and the Crown dependencies.: British nationality law governs mod ...
to document it in 1858, while on an expedition with Richard Francis Burton
Sir Richard Francis Burton (; 19 March 1821 – 20 October 1890) was a British explorer, writer, orientalist scholar,and soldier. He was famed for his travels and explorations in Asia, Africa, and the Americas, as well as his extraordinary kn ...
.
The lake is home to many species of fish which live nowhere else, especially cichlids. Invasive fish, such as the Nile perch
The Nile perch (''Lates niloticus''), also known as the African snook, Goliath perch, African barramundi , Goliath barramundi, Giant lates or the Victoria perch, is a species of freshwater fish in family Latidae of order Perciformes. It is wi ...
, have driven many endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found else ...
species to extinction
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ...
.
Geology
 Geologically, Lake Victoria is relatively young at about 400,000 years old. It formed when westward-flowing rivers were dammed by an upthrown crustal block. During the
Geologically, Lake Victoria is relatively young at about 400,000 years old. It formed when westward-flowing rivers were dammed by an upthrown crustal block. During the Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
era, what is now the catchment area of the lake was on the western side of an uplifted area that functioned as a continental divide, with streams on the western side flowing into the Congo River
The Congo River ( kg, Nzâdi Kôngo, french: Fleuve Congo, pt, Rio Congo), formerly also known as the Zaire River, is the second longest river in Africa, shorter only than the Nile, as well as the second largest river in the world by discharge ...
basin and streams on the eastern side flowing to the Indian Ocean. As the East African Rift System formed, the eastern wall of the Albertine Rift
The Albertine Rift is the western branch of the East African Rift, covering parts of Uganda, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), Rwanda, Burundi and Tanzania.
It extends from the northern end of Lake Albert to the southern end of Lake Tan ...
(or Western Rift) rose, gradually reversing the drainage towards what is now Lake Victoria. The opening of the main East African Rift and the Albertine Rift downwarped the area between them as the rift walls rose, creating the current Lake Victoria basin.
During its geological history, Lake Victoria went through changes ranging from its present shallow depression, through to what may have been a series of much smaller lakes. Geological cores taken from its bottom show Lake Victoria has dried up completely at least three times since it formed. These drying cycles are probably related to past ice ages, which were times when precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
declined globally. Lake Victoria last dried out about 17,300 years ago, and it refilled 14,700 years ago as the African humid period
The African humid period (AHP) (also known by other names) is a climate period in Africa during the late Pleistocene and Holocene geologic epochs, when northern Africa was wetter than today. The covering of much of the Sahara desert by grasses, ...
began.
Hydrology and limnology
Lake Victoria receives 80 percent of its water from direct rainfall. Average evaporation on the lake is between per year, almost double the precipitation ofriparian
A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the Earth. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks a ...
areas. Lake Victoria receives its water additionally from rivers, and thousands of small streams. The Kagera River
The Kagera River, also known as Akagera River, or Alexandra Nile, is an East African river, forming part of the upper headwaters of the Nile and carrying water from its most distant source.Stanley, H.M., 1899, Through the Dark Continent, London: G ...
is the largest river flowing into this lake, with its mouth on the lake's western shore. Lake Victoria is drained solely by the Nile River near Jinja, Uganda, on the lake's northern shore. In the Kenya sector, the main influent rivers are the Sio, Nzoia, Yala, Nyando, Sondu Miriu, Mogusi, and Migori
Luo people, Migori also known as Suna-Migori is a multi-ethnic municipal town which acts as the capital of Migori County, Kenya. The town is located 63 kilometers south of Kisii, Kenya, Kisii town and 22 km north of the Tanzanian borde ...
.
source of the Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest riv ...
, is more often considered to be one of the tributary rivers of the Kagera River (the exact tributary remains undetermined), and which originates in either Rwanda or Burundi. The uppermost section of the Nile is generally known as the Victoria Nile until it reaches Lake Albert. Although it is a part of the same river system known as the White Nile and is occasionally referred to as such, strictly speaking this name does not apply until after the river crosses the Uganda border into South Sudan to the north.
The lake exhibits eutrophic conditions. In 1990–1991, oxygen concentrations in the mixed layer were higher than in 1960–1961, with nearly continuous oxygen supersaturation in surface waters. Oxygen concentrations in hypolimnetic waters (i.e. the layer of water that lies below the thermocline
A thermocline (also known as the thermal layer or the metalimnion in lakes) is a thin but distinct layer in a large body of fluid (e.g. water, as in an ocean or lake; or air, e.g. an atmosphere) in which temperature changes more drastically with ...
, is noncirculating, and remains perpetually cold) were lower in 1990–1991 for a longer period than in 1960–1961, with values of less than 1 mg per litre (< 0.4 gr/cu ft) occurring in water as shallow as compared with a shallowest occurrence of greater than in 1961. The changes in oxygenation are considered consistent with measurements of higher algal biomass and productivity. These changes have arisen for multiple reasons: successive burning within its basin, soot and ash from which has been deposited over the lake's wide area; from increased nutrient inflows via rivers, and from increased pollution associated with settlement along its shores.
Between 2010 and 2022 the surface area of Lake Victoria increased by 15% flooding lakeside communities.
Bathymetry
 The lake is considered a shallow lake considering its large geographic area with a maximum depth of approximately and an average depth of . A 2016 project digitized ten-thousand points and created the first true bathymetric map of the lake. The deepest part of the lake is offset to the east of the lake near Kenya and the lake is generally shallower in the west along the Ugandan shoreline and the south along the Tanzanian shoreline.
The lake is considered a shallow lake considering its large geographic area with a maximum depth of approximately and an average depth of . A 2016 project digitized ten-thousand points and created the first true bathymetric map of the lake. The deepest part of the lake is offset to the east of the lake near Kenya and the lake is generally shallower in the west along the Ugandan shoreline and the south along the Tanzanian shoreline.
Native wildlife
Mammals
Many mammal species live in the region of Lake Victoria, and some of these are closely associated with the lake itself and the nearby wetlands. Among these are thehippopotamus
The hippopotamus ( ; : hippopotamuses or hippopotami; ''Hippopotamus amphibius''), also called the hippo, common hippopotamus, or river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of only two extan ...
, African clawless otter
The African clawless otter (''Aonyx capensis''), also known as the Cape clawless otter or groot otter, is the second-largest freshwater otter species. It inhabits permanent water bodies in savannah and lowland forest areas through most of sub- ...
, spotted-necked otter
The spotted-necked otter (''Hydrictis maculicollis''), or speckle-throated otter, is an otter native to sub-Saharan Africa.
Description
The spotted-necked otter is a relatively small species, with males measuring from nose to rump, and weigh ...
, marsh mongoose
The marsh mongoose (''Atilax paludinosus''), also known as the water mongoose or the vansire, is a medium-sized mongoose native to sub-Saharan Africa that inhabits foremost freshwater wetlands. It has been listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red L ...
, sitatunga
The sitatunga or marshbuck (''Tragelaphus spekii'') is a swamp-dwelling antelope found throughout central Africa, centering on the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo, Cameroon, parts of Southern Sudan, Equatorial Guinea ...
, bohor reedbuck
The bohor reedbuck (''Redunca redunca'') is an antelope native to central Africa. The animal is placed under the genus '' Redunca'' and in the family Bovidae. It was first described by German zoologist and botanist Peter Simon Pallas in 1767. ...
, defassa waterbuck
The waterbuck (''Kobus ellipsiprymnus'') is a large antelope found widely in sub-Saharan Africa. It is placed in the genus '' Kobus'' of the family Bovidae. It was first described by Irish naturalist William Ogilby in 1833. Its 13 subspecies ...
, cane rat
The genus ''Thryonomys'', also known as the cane rats or grasscutters, is a genus of rodent found throughout Africa south of the Sahara, the only members of the family Thryonomyidae. They are eaten in some African countries and are a pest species ...
s, and giant otter shrew
The giant otter shrew (''Potamogale velox'') is a semiaquatic, carnivorous afrotherian mammal. It is found in the main rainforest block of central Africa from Nigeria to Zambia, with a few isolated populations in Kenya and Uganda. It lives in str ...
.
Reptiles
Lake Victoria and its wetlands has a large population ofNile crocodile
The Nile crocodile (''Crocodylus niloticus'') is a large crocodilian native to freshwater habitats in Africa, where it is present in 26 countries. It is widely distributed throughout sub-Saharan Africa, occurring mostly in the central, eastern, ...
s, as well as African helmeted turtle
The African helmeted turtle (''Pelomedusa subrufa''), also known commonly as the marsh terrapin, the crocodile turtle, or in the pet trade as the African side-necked turtle, is a species of omnivorous side-necked terrapin in the family Pelomedus ...
s, variable mud turtles, and Williams' mud turtle.Spawls, Howell, Drewes, and Ashe (2002). ''A Field Guide to the Reptiles of East Africa''. Academic Press, London. . The Williams' mud turtle is restricted to Lake Victoria and other lakes, rivers, and swamps in the upper Nile basin.
Cichlid fish
 Lake Victoria formerly was very rich in fish, including many endemics, but a high percentage of these became extinct since the 1940s. The main group in Lake Victoria is the haplochromine cichlids (''
Lake Victoria formerly was very rich in fish, including many endemics, but a high percentage of these became extinct since the 1940s. The main group in Lake Victoria is the haplochromine cichlids (''Haplochromis
''Haplochromis'' is a ray-finned fish genus in the family Cichlidae. It has been used as the default " wastebin taxon" for Pseudocrenilabrinae cichlids of the East African Rift, and as such became the "largest" fish "genus". Many of these cichl ...
'' ''sensu lato
''Sensu'' is a Latin word meaning "in the sense of". It is used in a number of fields including biology, geology, linguistics, semiotics, and law. Commonly it refers to how strictly or loosely an expression is used in describing any particular c ...
'') with more than 500 species, almost all endemic,DeWeerdt, S. (28 February 2004)Dark secret of the lake.
New Scientist. Retrieved 26 March 2017. and including an estimated 300 that still are undescribed.Sayer, C.A., L. Máiz-Tomé, and W.R.T. Darwall (2018). Freshwater biodiversity in the Lake Victoria Basin: Guidance for species conservation, site protection,
climate resilience
Climate resilience is defined as the "capacity of social, economic and ecosystems to cope with a hazardous event or trend or disturbance".IPCC, 2022Summary for Policymakers .-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, M. Tignor, ...
and sustainable livelihoods. Cambridge, UK and Gland, Switzerland: IUCN. This is far more species of fish than any other lake in the world, except Lake Malawi
Lake Malawi, also known as Lake Nyasa in Tanzania and Lago Niassa in Mozambique, is an African Great Lake and the southernmost lake in the East African Rift system, located between Malawi, Mozambique and Tanzania.
It is the fifth largest fr ...
. These are the result of a rapid adaptive radiation
In evolutionary biology, adaptive radiation is a process in which organisms diversify rapidly from an ancestral species into a multitude of new forms, particularly when a change in the environment makes new resources available, alters biotic int ...
in the last circa 15,000 years. Their extraordinary diversity and speed of evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
have been the subjects for many scientists studying the forces that drive the richness of life everywhere. The Victoria haplochromines are part of an older group of more than 700 closely related species, also including those of several smaller lakes in the region, notably Kyoga, Edward–George
George may refer to:
People
* George (given name)
* George (surname)
* George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George
* George Washington, First President of the United States
* George W. Bush, 43rd Presid ...
, Albert, and Kivu
Kivu was the name for a large "region" in the Democratic Republic of the Congo under the rule of Mobutu Sese Seko that bordered Lake Kivu. It included three "Sub-Regions" ("Sous-Régions" in French): Nord-Kivu, Sud-Kivu and Maniema, correspondi ...
.
Most of these lakes are relatively shallow (like Victoria) and part of the present-day upper Nile basin. The exception is Lake Kivu, which is part of the present-day Congo River basin
The Congo River ( kg, Nzâdi Kôngo, french: Fleuve Congo, pt, Rio Congo), formerly also known as the Zaire River, is the second longest river in Africa, shorter only than the Nile, as well as the second largest river in the world by discharge ...
, but is believed to have been connected to Lakes Edward and Victoria by rivers until the uplifting of parts of the East African Rift. This deep lake may have functioned as an "evolutionary reservoir" for this haplochromine group in periods where other shallower lakes in the region dried out, as happened to Lake Victoria about 15,000 years ago. In recent history only Lake Kyoga was easily accessible to Victoria cichlids, as further downstream movement by the Victoria Nile
The White Nile ( ar, النيل الأبيض ') is a river in Africa, one of the two main tributaries of the Nile, the other being the Blue Nile. The name comes from the clay sediment carried in the water that changes the water to a pale color. ...
(to Lake Albert) is prevented by a series of waterfalls, notably Murchison. In contrast, the Owen Falls
The Owen Falls was a waterfall on the White Nile in Uganda near the city of Jinja. The falls, together with the nearby Ripon Falls, were submerged in 1954 with the completion of the Nalubaale Hydroelectric Power Station. The dam that houses ...
(now flooded by a dam
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use ...
) between Victoria and Kyoga were essentially a series of rapids that did not effectively block fish movements between the two lakes.
 The Victoria haplochromines are distinctly
The Victoria haplochromines are distinctly sexually dimorphic
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most ani ...
(males relatively brightly colored; females dull), and their ecology is extremely diverse, falling into at least 16 groups, including detritivores, zooplanktivores, insectivores, prawn-eaters, molluscivore A molluscivore is a carnivorous animal that specialises in feeding on molluscs such as gastropods, bivalves, brachiopods and cephalopods. Known molluscivores include numerous predatory (and often cannibalistic) molluscs, (e.g.octopuses, murexes, d ...
s and piscivore
A piscivore () is a carnivorous animal that eats primarily fish. The name ''piscivore'' is derived . Piscivore is equivalent to the Greek-derived word ichthyophage, both of which mean "fish eater". Fish were the diet of early tetrapod evoluti ...
s. As a result of predation by the introduced Nile perch
The Nile perch (''Lates niloticus''), also known as the African snook, Goliath perch, African barramundi , Goliath barramundi, Giant lates or the Victoria perch, is a species of freshwater fish in family Latidae of order Perciformes. It is wi ...
, eutrophication
Eutrophication is the process by which an entire body of water, or parts of it, becomes progressively enriched with minerals and nutrients, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus. It has also been defined as "nutrient-induced increase in phytopla ...
and other changes to the ecosystem, it is estimated that at least 200 species (about 40 percent) of Lake Victoria haplochromines have become extinct, including more than 100 undescribed species. Initially it was feared that this number was even higher, by some estimates 65 percent of the total species, but several species that were feared extinct have been rediscovered after the Nile perch started to decline in the 1990s.IUCN Red ListsGeographic Patterns
Eastern Africa. Retrieved 25 March 2017. Several of the remaining species are seriously threatened and additional extinctions are possible.Fiedler, P.L. and P M. Kareiva, editors (1998). Conservation Biology: For the Coming Decade. 2nd edition. pp. 209–10. Some species have survived in nearby small satellite lakes, have survived in refugias among rocks or
papyrus sedge
''Cyperus papyrus'', better known by the common names papyrus, papyrus sedge, paper reed, Indian matting plant, or Nile grass, is a species of aquatic flowering plant belonging to the sedge family Cyperaceae. It is a tender herbaceous perennia ...
s (protecting them from the Nile perch), or have adapted to the human-induced changes in the lake itself. Such adaptions include a larger gill
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are ...
area (adaption for oxygen-poor water), changes in the feeding apparatus, changes to the eyes (giving them a better sight in turbid water) and smaller head/larger caudal peduncle
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as see ...
(allowing faster swimming). The piscivorous (affected by both predation and competition from Nile perch), molluscivorous and insectivorous haplochromines were particularly hard hit with many extinctions. Others have become extinct in their pure form, but survive as hybrids between close relatives (especially among the detritivores). The zooplanktivores have been least affected and in the late 1990s had reached densities similar to, or above, the densities before the drastic declines, although consisting of fewer species and often switching their diet towards macroinvertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate ...
s. Some of the threatened Lake Victoria cichlid species have captive "insurance" populations in zoos, public aquaria
A public aquarium (plural: ''public aquaria'' or ''public Water Zoo'') is the aquatic counterpart of a zoo, which houses living aquatic animal and plant specimens for public viewing. Most public aquariums feature tanks larger than those kept b ...
and among private aquarists, and a few species are extinct in the wild (only survive in captivity).
Before the mass extinction that has occurred among the lake's cichlids in the last 50 years, about 90 percent of the native fish species in the lake were haplochromines. Disregarding the haplochromines, the only native Victoria cichlids are two critically endangered tilapia, the Singida tilapia
''Oreochromis esculentus'', the Singida tilapia or Graham's tilapia, is a species of cichlid endemic to the Lake Victoria basin, including some of its satellite lakes such as Kyoga, in Tanzania, Uganda, and Kenya. Its common name refers to ...
or ''ngege'' (''Oreochromis esculentus'') and Victoria tilapia
''Oreochromis variabilis'', the Victoria tilapia, is a species of African cichlid native to Lake Victoria and its tributaries, Lake Kyoga, Lake Kwania, and Lake Bisina (Salisbury), as well as being found in the Victoria Nile above Murchison Fal ...
(''O. variabilis'').
In 1927–1928 Michael Graham conducted the first ever systematic Fisheries Survey of Lake Victoria
Lake Victoria supports Africa's largest inland fishery, with the majority of present catch being the invasive Nile perch, introduced to the Lake in the 1950s. Prior to the introduction of Nile perch as well as Nile tilapia, the fish community w ...
. In his official report of the expedition, Graham wrote that "The ngege or satu ''Tilapia esculenta'', is the most important food fish of the lake, whether for native or non-native consumption. No other fish equals it in the quality of the flesh. It is convenient size for trade, travels well and is found in much greater numbers than other important fish, such as semutundu (Luganda), ''Bagrus sp.''".Graham M. (1929.) The Victoria Nyanza and Its Fisheries: A Report on the Fish Survey of Lake Victoria 1927–1928 and Appendices. London: Crown Agents for the Colonies. 256pp. Furthermore, Graham noted that the introduction of the European flax gill net
Gillnetting is a fishing method that uses gillnets: vertical panels of netting that hang from a line with regularly spaced floaters that hold the line on the surface of the water. The floats are sometimes called "corks" and the line with corks is ...
of 5 inch mesh had undoubtedly caused a diminution in the number of ngege in those parts of the Kavirondo Gulf, the northern shore of the lake, the Sesse Islands and Smith's Sound which are conveniently situated close to markets. Survey catches in 1927–28 included several Haplochromis
''Haplochromis'' is a ray-finned fish genus in the family Cichlidae. It has been used as the default " wastebin taxon" for Pseudocrenilabrinae cichlids of the East African Rift, and as such became the "largest" fish "genus". Many of these cichl ...
species that are now thought to be extinct, including: ''Haplochromis flavipinnis
''Haplochromis flavipinnis'' is a species of cichlid endemic to Lake Victoria
Lake Victoria is one of the African Great Lakes. With a surface area of approximately , Lake Victoria is Africa's largest lake by area, the world's largest trop ...
'', '' Haplochromis gowersii'', '' Haplochromis longirostris'', ''Haplochromis macrognathus
''Haplochromis macrognathus'' is a species of cichlid fish endemic to Lake Victoria in East Africa. This piscivorous
A piscivore () is a carnivorous animal that eats primarily fish. The name ''piscivore'' is derived . Piscivore is equiva ...
'', ''Haplochromis michaeli
''Haplochromis michaeli'' is a species of cichlid endemic to Lake Victoria though it may now be extinct. This species can reach a length of SL. The specific name honours the collector of the type, the British fisheries scientist
Fisheries ...
'', '' Haplochromis nigrescens'', '' Haplochromis prognathus''.
As well as being due to the introduction of Nile Perch
The Nile perch (''Lates niloticus''), also known as the African snook, Goliath perch, African barramundi , Goliath barramundi, Giant lates or the Victoria perch, is a species of freshwater fish in family Latidae of order Perciformes. It is wi ...
, the extinction of cichlids in the genus ''Haplochromis
''Haplochromis'' is a ray-finned fish genus in the family Cichlidae. It has been used as the default " wastebin taxon" for Pseudocrenilabrinae cichlids of the East African Rift, and as such became the "largest" fish "genus". Many of these cichl ...
'' has also been blamed on the lake's eutrophication. The fertility of tropical waters depends on the rate at which nutrients can be brought into solution. The influent rivers of Lake Victoria provide few nutrients to the lake in relation to its size. Because of this, most of Lake Victoria's nutrients are thought to be locked up in lake-bottom deposits. By itself, this vegetative matter decays slowly. Animal flesh decays considerably faster, however, so the fertility of the lake is dependent on the rate at which these nutrients can be taken up by fish and other organisms. There is little doubt that ''Haplochromis'' played an important role in returning detritus and plankton back into solution. With some 80 percent of ''Haplochromis'' species feeding off detritus, and equally capable of feeding off one another, they represented a tight, internal recycling system, moving nutrients and biomass both vertically and horizontally through the water column, and even out of the lake via predation by humans and terrestrial animals. The removal of ''Haplochromis'', however, may have contributed to the increasing frequency of algal bloom
An algal bloom or algae bloom is a rapid increase or accumulation in the population of algae in freshwater or marine water systems. It is often recognized by the discoloration in the water from the algae's pigments. The term ''algae'' encompass ...
s, which may in turn be responsible for mass fish kills.
Other fish
The non-cichlid native fish include African tetras ('' Brycinus''), cyprinids (''Enteromius
''Enteromius'' is a genus of small to medium-sized cyprinid fish native to tropical Africa. Most species were placed in the genus ''Barbus
''Barbus'' is a genus of ray-finned fish in the family Cyprinidae. The type species of ''Barbus'' is ...
'', ''Garra
''Garra'' is a genus of fish in the family Cyprinidae. These fish are one example of the "log suckers", sucker-mouthed barbs and other cyprinids commonly kept in aquaria to keep down algae. The doctor fish of Anatolia and the Middle East belo ...
'', ''Labeo
''Labeo'' is a genus of carps in the family Cyprinidae. They are found in freshwater habitats in the tropics and subtropics of Africa and Asia.
It contains the typical labeos in the subfamily Labeoninae, which may not be a valid group, however ...
'', ''Labeobarbus
''Labeobarbus'' is a mid-sized ray-finned fish genus in the family Cyprinidae. Its species are widely distributed throughout eastern Africa and especially southern Africa, but also in Lake Tana in Ethiopia. A common name, in particular for the s ...
'', ''Rastrineobola
The silver cyprinid (''Rastrineobola argentea'') also known as the Lake Victoria sardine, mukene,and omena (native language), dagaa (swahili language) is a species of pelagic, freshwater ray-finned fish in the carp family, Cyprinidae from East A ...
'' and '' Xenobarbus''), airbreathing catfish ('' Clariallabes'', ''Clarias
''Clarias'' is a genus of catfishes (order Siluriformes) of the family Clariidae, the airbreathing catfishes. The name is derived from the Greek ''chlaros'', which means lively, in reference to the ability of the fish to live for a long time out ...
'' and ''Xenoclarias
The Lake Victoria deepwater catfish (''Xenoclarias eupogon'') is a species of catfish ( order Siluriformes) of the family Clariidae. It is monotypic within the genus ''Xenoclarias''. This species is endemic to Lake Victoria, and is found in dee ...
''), bagrid catfish ('' Bagrus''), loach catfish (''Amphilius
''Amphilius'' is a genus of catfishes of the family Amphiliidae.
''Amphilius'' catfish have fairly lengthened bodies, with short, depressed, and broad heads. They have three pairs of fringed barbels. The eyes, small and located dorsally, are v ...
'' and '' Zaireichthys''), silver butter catfish (''Schilbe intermedius''), '' Synodontis'' squeaker catfish, ''Nothobranchius
''Nothobranchius'' is a genus of small, freshwater killifish, classified in either the family Nothobranchiidaevan der Laan, R., Eschmeyer, W.N. & Fricke, R. (2014)Family-group names of Recent fishes.''Zootaxa, 3882 (2): 1–230.'' or a more inc ...
'' killifish, poeciliids ('' Aplocheilichthys'' and ''Micropanchax
''Micropanchax'' is a genus of poeciliids native to Africa.
Species
The 13 recognized species in this genus are:
* ''Micropanchax antinorii'' (Vinciguerra, 1883) (black lampeye)
* ''Micropanchax bracheti'' (Heinz Otto Berkenkamp, Berkenkamp, 19 ...
''), the spiny eel ''Mastacembelus
''Mastacembelus'' is a genus of many species of spiny eel fish from the family Mastacembelidae. They are native to Africa (c. 45 species) and Asia (c. 15 species). Most are found in rivers and associated systems (even in rapids), but there are ...
frenatus'', elephantfish ('' Gnathonemus'', ''Hippopotamyrus
''Hippopotamyrus'' is a genus of elephantfish in the family Mormyridae.
Species
There are currently 11 recognized species in this genus:
* '' Hippopotamyrus ansorgii'' ( Boulenger 1905) (Slender stonebasher)
* '' Hippopotamyrus castor'' Pappe ...
'', ''Marcusenius
''Marcusenius'' is a genus of elephantfishes native to Africa. Its members are highly diverse in size, with the smallest species reaching less than and the largest more than .
The genus is named after Johann Marcusen.
Species
There are cur ...
'', ''Mormyrus
''Mormyrus'' is a genus of ray-finned fish in the family Mormyridae.
Species
There are currently 22 recognized species in this genus:
* '' Mormyrus bernhardi'' Pellegrin 1926 (Bernhard's elephant-snout fish)
* '' Mormyrus caballus'' Boul ...
'', ''Petrocephalus
''Petrocephalus'' is a genus of ray-finned fish in the family (biology), family Mormyridae. All the fish species of this genus are endemism, endemic to Africa.
Species
There are currently 46 recognized species in this genus:
* ''Petrocephalus a ...
'', and '' Pollimyrus''), the climbing gourami ''Ctenopoma
''Ctenopoma'' is a genus of climbing gouramies native to Africa. ''Microctenopoma'' has been included in ''Ctenopoma'' in the past; in contrast to that genus, ''Ctenopoma'' species are egg scatterers with no parental care.
Species
The 18 current ...
muriei'' and marbled lungfish
The marbled lungfish (''Protopterus aethiopicus'') is a lungfish of the family Protopteridae. Also known as the leopard lungfish, it is found in Eastern and Central Africa, as well as the Nile region. At 133 billion base pairs, it has the large ...
(''Protopterus aethiopicus'').FishBaseFish Species in Victoria.
Retrieved 25 March 2017. At a genus level, most of these are widespread in Africa, but the very rare ''Xenobarbus'' and ''Xenoclarias'' are endemic to the lake, and the common ''Rastrineobola'' is near-endemic.
Crustaceans
Four species of freshwater crabs are known from Lake Victoria: '' Potamonautes niloticus'' is widespread in the lake and '' P. emini'' has been recorded from the vicinity ofBukoba
Bukoba is a city with a population of 128,796 (2012 census), situated in the north west of Tanzania on the south western shores of Lake Victoria. It is the capital of the Kagera region, and the administrative seat for Bukoba Urban District. ...
in Tanzania, but both are also found elsewhere in Africa. The last were first scientifically described in 2017 and very little is known about them: '' P. entebbe'' is only known from near Entebbe
Entebbe is a city in Central Uganda. Located on a Lake Victoria peninsula, approximately southwest of the Ugandan capital city, Kampala. Entebbe was once the seat of government for the Protectorate of Uganda prior to independence, in 1962. T ...
(the only known specimen was collected in 1955 and it is unknown if it was in or near the lake) and '' P. busungwe'' only at Busungwe Island in the northwestern part of the lake. The latter likely is the smallest African freshwater crab with a carapace width up to about , although '' P. kantsyore'' of Kagera River
The Kagera River, also known as Akagera River, or Alexandra Nile, is an East African river, forming part of the upper headwaters of the Nile and carrying water from its most distant source.Stanley, H.M., 1899, Through the Dark Continent, London: G ...
, and ''Platythelphusa
''Platythelphusa'' is a genus of freshwater crabs endemism, endemic to Lake Tanganyika. It has been placed in a number of families, including a monotypic family (biology), family, Platythelphusidae, as well as Potamidae and its current position i ...
maculata'' and ''P. polita'' of Lake Tanganyika are almost as small.
The only shrimp/prawn is ''Caridina nilotica
''Caridina nilotica'' is a species of freshwater shrimp in the family Atyidae. It is native to Africa from the River Nile in Egypt to Lake Sibaya, South Africa, and is the only species of shrimp in Lake Victoria
Lake Victoria is one of th ...
'', which is common and widespread in Lake Victoria.
Molluscs
Lake Victoria is home to 28 species of freshwater snails (e.g., ''Bellamya
''Bellamya'' was a supertanker, built in 1976 by Chantiers de l'Atlantique at Saint-Nazaire for the French branch of Shell Oil. She was the second Batillus class supertanker. ''Bellamya'', together with her sister ships ''Batillus, Pierre Guil ...
'', ''Biomphalaria
''Biomphalaria'' is a genus of air-breathing freshwater snails, aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the family Planorbidae, the ram's horn snails and their allies.MolluscaBase (2018). Biomphalaria Preston, 1910. Accessed through: World Regi ...
'', ''Bulinus
''Bulinus'' is a genus of small tropical freshwater snails, aquatic gastropod mollusks in the family Bulinidae, the ramshorn snails and their allies. MolluscaBase eds. (2020). MolluscaBase. Bulinus O. F. Müller, 1781. Accessed through: World ...
'', '' Cleopatra'', ''Gabbiella
''Gabbiella'' is an East African genus of small freshwater snails with an operculum, aquatic prosobranch gastropod mollusks in the family Bithyniidae
Bithyniidae is a family of small freshwater snails with an operculum, aquatic gastropod ...
'', and ''Melanoides
''Melanoides'' is a genus of freshwater snail with an operculum, an aquatic gastropod mollusk in the subfamily Thiarinae of the family Thiaridae.Bouchet, P. (2014). Melanoides Olivier, 1804. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species ...
''), including 12 endemic species/subspecies. There are 17 species of bivalves (''Corbicula
''Corbicula'' is a genus of freshwater and brackish water clams, aquatic bivalve mollusks in the family Cyrenidae, the basket clams.Gofas, S. (2015). Cyrenidae Gray, 1847. In: MolluscaBase (2015). Accessed through: World Register of Marine Spe ...
'', ''Coelatura
''Coelatura'' is a genus of bivalve in the Unionidae family.
Species
Species:
*''Coelatura aegyptiaca''
*''Coelatura alluaudi''
*''Coelatura bakeri''
*''Coelatura briarti''
*''Coelatura choziensis''
*''Coelatura cridlandi''
*''Coelatura d ...
'', ''Sphaerium
''Sphaerium'' is a genus of very small freshwater clams, aquatic bivalve molluscs in the family Sphaeriidae, known as the fingernail clams. The small clams in this genus are unusual in that many of them, such as '' Sphaerium corneum'', can climb ...
'', and '' Byssanodonta''), including 6 endemic species/subspecies. It is likely that undescribed species of snails remain. Conversely, genetic studies indicate that some morphologically distinctive populations, traditionally regarded as separate species, may only be variants of single species. Two of the snail genera, ''Biomphalaria'' and ''Bulinus'', are intermediate hosts of the parasite that causes bilharzia
Schistosomiasis, also known as snail fever, bilharzia, and Katayama fever, is a disease caused by parasitic flatworms called schistosomes. The urinary tract or the intestines may be infected. Symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, bloody ...
(schistosomiasis). Human infections by this parasite are common at Lake Victoria. This may increase as a result of the spread of the invasive water hyacinth (an optimum snail habitat), and the loss of many snail-eating cichlids in the lake.
Spiders
''Evarcha culicivora
''Evarcha culicivora'' is a species of jumping spider (family Salticidae) found only around Lake Victoria in Kenya and Uganda. At maturity, ''E. culicivora'' spiders have an average size of 5 mm for both males and females. The range in ...
'' is a species of jumping spider (family Salticidae
Jumping spiders are a group of spiders that constitute the family Salticidae. As of 2019, this family contained over 600 described genera and over 6,000 described species, making it the largest family of spiders at 13% of all species. Jumping spi ...
) found only around Lake Victoria in Kenya and Uganda. It feeds primarily on female mosquitos.
Fisheries
 Lake Victoria supports Africa's largest inland fishery (as of 1997). Initially the fishery involved native species, especially tilapia and haplochromine cichlids, but also catfish (''Bagrus'', ''Clarias'', ''Synodontis'' and silver butter catfish), elephantfish, ningu (''Labeo victorianus'') and marbled lungfish (''Protopterus aethiopicus'').Lake Victoria Fisheries Organization (2016). Some of these, including tilapia and ningu (''Labeo victorianus''), had already declined in the first half of the 20th century due to overfishing. To boost fishing, several species of non-native tilapia and Nile perch were introduced to the lake in the 1950s. Nevertheless, the natives continued to dominate fisheries until the 1970s where their decline meant that there was a strong shift towards the non-native Nile tilapia (now 7 percent of catches), non-native Nile perch (60 percent) and the native Lake Victoria sardine (30 percent). Because of its small size, the abundant open-water Lake Victoria sardine only supported minor fisheries until the decline of other natives. At the peak in the early 1990s, of Nile perch were landed annually in Lake Victoria, but this has declined significantly in later years.
Lake Victoria supports Africa's largest inland fishery (as of 1997). Initially the fishery involved native species, especially tilapia and haplochromine cichlids, but also catfish (''Bagrus'', ''Clarias'', ''Synodontis'' and silver butter catfish), elephantfish, ningu (''Labeo victorianus'') and marbled lungfish (''Protopterus aethiopicus'').Lake Victoria Fisheries Organization (2016). Some of these, including tilapia and ningu (''Labeo victorianus''), had already declined in the first half of the 20th century due to overfishing. To boost fishing, several species of non-native tilapia and Nile perch were introduced to the lake in the 1950s. Nevertheless, the natives continued to dominate fisheries until the 1970s where their decline meant that there was a strong shift towards the non-native Nile tilapia (now 7 percent of catches), non-native Nile perch (60 percent) and the native Lake Victoria sardine (30 percent). Because of its small size, the abundant open-water Lake Victoria sardine only supported minor fisheries until the decline of other natives. At the peak in the early 1990s, of Nile perch were landed annually in Lake Victoria, but this has declined significantly in later years.
Environmental issues
A number of environmental issues are associated with Lake Victoria and the complete disappearance of many endemic cichlid species has been called the "most dramatic example of human-caused extinctions within an ecosystem".Invasive fish
Starting in the 1950s, many species have been Introduced species, introduced to Lake Victoria where they have become Invasive species, invasive and a prime reason for the extinction of many endemic haplochromine cichlids. Among the introductions are several tilapias: Redbreast tilapia, redbreast (''Coptodon rendalli''), Redbelly tilapia, redbelly (''C. zillii''), Nile (''Oreochromis niloticus'') and Oreochromis leucostictus, blue-spotted tilapias (''O. leucostictus'').Pringle, R.M. (2005)The Origins of the Nile Perch in Lake Victoria.
BioScience 55 (9): 780–787. Although these have contributed to the extinction of native fish by causing significant changes to the ecosystem, outcompeted natives and (in the case of the Nile tilapia) possibly hybridized with the highly threatened native tilapias, the most infamous introduction was the large and highly predatory
Nile perch
The Nile perch (''Lates niloticus''), also known as the African snook, Goliath perch, African barramundi , Goliath barramundi, Giant lates or the Victoria perch, is a species of freshwater fish in family Latidae of order Perciformes. It is wi ...
(''Lates niloticus'').
 As early as the 1920s, it was proposed to introduce a large pelagic predator such as the Nile perch to improve the fisheries in the lake. At the same time it was warned that this could present a serious danger to the native fish species and required extensive research into possible ecological effects before done. These warnings primarily concerned the native tilapia ''O. esculentus'', as the smaller haplochromine cichlids (despite playing an important role in local fisheries) were regarded as "trash fish" by the colonial government. In the following decades, the pressure to introduce the Nile perch continued, as did warnings about the possible effects of doing it. The first introduction of Nile perch to the region, done by the Uganda Game and Fisheries Department (then part of the colonial government) and local African fish guards, happened upstream of Murchison Falls directly after the completion of the Owen Falls Dam in 1954. This allowed it to spread to Lake Kyoga where additional Nile perch were released in 1955, but not Victoria itself. Scientists argued that further introduction should wait until research showed the effect of the introduction in Kyoga, but by the late 1950s, Nile perch began being caught in Lake Victoria. As the species was already present, there were few objections when more Nile perch were transferred to Victoria to further bolster the stock in 1962–63.
The origin of the first Victoria introductions in the 1950s is not entirely clear and indisputable evidence is lacking. Uganda Game and Fisheries Department (UGFD) officials denied that they were involved, but circumstantial evidence suggests otherwise and local Africans employed by UGFD have said that they introduced the species in 1954–55 under the directive of senior officials. UGFD officials argued that Nile perch must have spread to Lake Victoria by themselves by passing through the Owen Falls Dam when shut down for maintenance, but this is considered highly unlikely by many scientists. The Nile perch had spread throughout the lake by 1970. Initially the population of the Nile perch was relatively low, but a drastic increase happened, peaking in the 1980s, followed by a decline starting in the 1990s.
Due to the presence of the Nile perch, the natural balance of the lake's ecosystem has been disrupted. The food chain is being altered and in some cases, broken by the indiscriminate eating habits of the Nile perch.
The subsequent decrease in the number of algae-eating fish allows the algae to grow at an alarming rate, thereby choking the lake. The increasing amounts of algae, in turn, increase the amount of detritus (dead plant material) that falls to the deeper portions of the lake before decomposing. As a by-product of this the oxygen levels in the deeper layer of water are being depleted. Without oxygen, any aerobic life (such as fish) cannot exist in the deeper parts of the lake, forcing all life to exist within a narrow range of depth. In this way, the Nile perch has degraded the diverse and thriving ecosystem that was once Lake Victoria. The abundance of aquatic life is not the only dependent of the lake: more than thirty million people in Tanzania, Kenya and Uganda rely on the lake for its natural resources.
Hundreds of endemic species that evolved under the special conditions offered by the protection of Lake Victoria have been lost due to extinction, and several more are still threatened. Their loss is devastating for the lake, the fields of ecology, genetics and evolution biology, and more evidently, for the local fisheries. Local fisheries once depended on catching the lungfish, tilapia, carp and catfish that comprise the local diet.
Today, the composition and yields of such fish catches are virtually negligible. Extensive fish kills, Nile perch, loss of habitat and overfishing have caused many fisheries to collapse and many protein sources to be unavailable at the market for local consumption. Few fisheries, though, have been able to make the switch to catching the Nile perch, since that requires a significant amount of capital resources.
As early as the 1920s, it was proposed to introduce a large pelagic predator such as the Nile perch to improve the fisheries in the lake. At the same time it was warned that this could present a serious danger to the native fish species and required extensive research into possible ecological effects before done. These warnings primarily concerned the native tilapia ''O. esculentus'', as the smaller haplochromine cichlids (despite playing an important role in local fisheries) were regarded as "trash fish" by the colonial government. In the following decades, the pressure to introduce the Nile perch continued, as did warnings about the possible effects of doing it. The first introduction of Nile perch to the region, done by the Uganda Game and Fisheries Department (then part of the colonial government) and local African fish guards, happened upstream of Murchison Falls directly after the completion of the Owen Falls Dam in 1954. This allowed it to spread to Lake Kyoga where additional Nile perch were released in 1955, but not Victoria itself. Scientists argued that further introduction should wait until research showed the effect of the introduction in Kyoga, but by the late 1950s, Nile perch began being caught in Lake Victoria. As the species was already present, there were few objections when more Nile perch were transferred to Victoria to further bolster the stock in 1962–63.
The origin of the first Victoria introductions in the 1950s is not entirely clear and indisputable evidence is lacking. Uganda Game and Fisheries Department (UGFD) officials denied that they were involved, but circumstantial evidence suggests otherwise and local Africans employed by UGFD have said that they introduced the species in 1954–55 under the directive of senior officials. UGFD officials argued that Nile perch must have spread to Lake Victoria by themselves by passing through the Owen Falls Dam when shut down for maintenance, but this is considered highly unlikely by many scientists. The Nile perch had spread throughout the lake by 1970. Initially the population of the Nile perch was relatively low, but a drastic increase happened, peaking in the 1980s, followed by a decline starting in the 1990s.
Due to the presence of the Nile perch, the natural balance of the lake's ecosystem has been disrupted. The food chain is being altered and in some cases, broken by the indiscriminate eating habits of the Nile perch.
The subsequent decrease in the number of algae-eating fish allows the algae to grow at an alarming rate, thereby choking the lake. The increasing amounts of algae, in turn, increase the amount of detritus (dead plant material) that falls to the deeper portions of the lake before decomposing. As a by-product of this the oxygen levels in the deeper layer of water are being depleted. Without oxygen, any aerobic life (such as fish) cannot exist in the deeper parts of the lake, forcing all life to exist within a narrow range of depth. In this way, the Nile perch has degraded the diverse and thriving ecosystem that was once Lake Victoria. The abundance of aquatic life is not the only dependent of the lake: more than thirty million people in Tanzania, Kenya and Uganda rely on the lake for its natural resources.
Hundreds of endemic species that evolved under the special conditions offered by the protection of Lake Victoria have been lost due to extinction, and several more are still threatened. Their loss is devastating for the lake, the fields of ecology, genetics and evolution biology, and more evidently, for the local fisheries. Local fisheries once depended on catching the lungfish, tilapia, carp and catfish that comprise the local diet.
Today, the composition and yields of such fish catches are virtually negligible. Extensive fish kills, Nile perch, loss of habitat and overfishing have caused many fisheries to collapse and many protein sources to be unavailable at the market for local consumption. Few fisheries, though, have been able to make the switch to catching the Nile perch, since that requires a significant amount of capital resources.
Water hyacinth invasion
 The water hyacinth has become a major invasive plant species in Lake Victoria.
The release of large amounts of untreated wastewater (sewage) and agricultural and industrial runoff directly into Lake Victoria over the past 30 years has greatly increased the nutrient levels of nitrogen and phosphorus in the lake "triggering massive growth of exotic water hyacinth, which colonised the lake in the late 1990s".Luilo, G.B. (August 01, 2008). Lake Victoria water resources management challenges and prospects: a need for equitable and sustainable institutional and regulatory frameworks ''African Journal of Aquatic Science'' 33, 2, 105–13. This invasive weed creates anoxic (total depletion of oxygen levels) conditions in the lake inhibiting decomposing plant material, raising toxicity and disease levels to both fish and people. At the same time, the plant's mat or "web" creates a barrier for boats and ferries to maneuver, impedes access to the shoreline, interferes with hydroelectric power generation, and blocks the intake of water for industries.Kateregga, E., & Sterner, T. (January 01, 2009). "Lake Victoria Fish Stocks and the Effects of Water Hyacinth". ''Journal of Environment & Development'', 18, 1, 62–78.Albright, T.P., Moorhouse, T.G., & McNabb, T.J. (January 1, 2004). "The Rise and Fall of Water Hyacinth in Lake Victoria and the Kagera River Basin, 1989-2001". ''Journal of Aquatic Plant Management'', 42, 73–84. On the other hand, water hyacinth mats can potentially have a positive effect on fish life in that they create a barrier to overfishing and allow for fish growth, there has even been the reappearance of some fish species thought to have been extinct in recent years. The overall effects of the water hyacinth, however, are still unknown.
Growth of the water hyacinth in Lake Victoria has been tracked since 1993, reaching its maxima biomass in 1997 and then declining again by the end of 2001. Greater growth was observed in the northern part of the lake, in relatively protected areas, which may be linked to current and weather patterns and could also be due to the climate and water conditions, which are more suitable to the plants growth (as there are large urban areas to the north end of the lake, in Uganda). The invasive weed was first attempted to be controlled by hand, removed manually from the lake; however, re-growth occurred quickly. Public awareness exercises were also conducted. More recently, measures have been used such as the introduction of natural insect predators, including two different water hyacinth weevils and large harvesting and chopping boats, which seem to be much more effective in eliminating the water hyacinth. A green power plant that uses harvested water hyacinth (but also can use other degradable waste) was constructed in Kisumu County in 2013. In addition to the biogas it produces, its by-product can be used as fertilizer.
Other factors which may have contributed to the decline of the water hyacinth in Lake Victoria include varying weather patterns, such as El Niño during the last few months of 1997 and first six months of 1998 bringing with it higher levels of water in the lake and thus dislodging the plants. Heavy winds and rains along with their subsequent waves may have also damaged the plants during this same time frame. The plants may not have been destroyed, instead merely moved to another location. Additionally, the water quality, nutrient supply, temperature, and other environmental factors could have played a role. Overall, the timing of the decline could be linked to all of these factors and perhaps together, in combination, they were more effective than any one deterrent would have been by itself. The water hyacinth is in remission and this trend could be permanent if control efforts are continued.
The water hyacinth has become a major invasive plant species in Lake Victoria.
The release of large amounts of untreated wastewater (sewage) and agricultural and industrial runoff directly into Lake Victoria over the past 30 years has greatly increased the nutrient levels of nitrogen and phosphorus in the lake "triggering massive growth of exotic water hyacinth, which colonised the lake in the late 1990s".Luilo, G.B. (August 01, 2008). Lake Victoria water resources management challenges and prospects: a need for equitable and sustainable institutional and regulatory frameworks ''African Journal of Aquatic Science'' 33, 2, 105–13. This invasive weed creates anoxic (total depletion of oxygen levels) conditions in the lake inhibiting decomposing plant material, raising toxicity and disease levels to both fish and people. At the same time, the plant's mat or "web" creates a barrier for boats and ferries to maneuver, impedes access to the shoreline, interferes with hydroelectric power generation, and blocks the intake of water for industries.Kateregga, E., & Sterner, T. (January 01, 2009). "Lake Victoria Fish Stocks and the Effects of Water Hyacinth". ''Journal of Environment & Development'', 18, 1, 62–78.Albright, T.P., Moorhouse, T.G., & McNabb, T.J. (January 1, 2004). "The Rise and Fall of Water Hyacinth in Lake Victoria and the Kagera River Basin, 1989-2001". ''Journal of Aquatic Plant Management'', 42, 73–84. On the other hand, water hyacinth mats can potentially have a positive effect on fish life in that they create a barrier to overfishing and allow for fish growth, there has even been the reappearance of some fish species thought to have been extinct in recent years. The overall effects of the water hyacinth, however, are still unknown.
Growth of the water hyacinth in Lake Victoria has been tracked since 1993, reaching its maxima biomass in 1997 and then declining again by the end of 2001. Greater growth was observed in the northern part of the lake, in relatively protected areas, which may be linked to current and weather patterns and could also be due to the climate and water conditions, which are more suitable to the plants growth (as there are large urban areas to the north end of the lake, in Uganda). The invasive weed was first attempted to be controlled by hand, removed manually from the lake; however, re-growth occurred quickly. Public awareness exercises were also conducted. More recently, measures have been used such as the introduction of natural insect predators, including two different water hyacinth weevils and large harvesting and chopping boats, which seem to be much more effective in eliminating the water hyacinth. A green power plant that uses harvested water hyacinth (but also can use other degradable waste) was constructed in Kisumu County in 2013. In addition to the biogas it produces, its by-product can be used as fertilizer.
Other factors which may have contributed to the decline of the water hyacinth in Lake Victoria include varying weather patterns, such as El Niño during the last few months of 1997 and first six months of 1998 bringing with it higher levels of water in the lake and thus dislodging the plants. Heavy winds and rains along with their subsequent waves may have also damaged the plants during this same time frame. The plants may not have been destroyed, instead merely moved to another location. Additionally, the water quality, nutrient supply, temperature, and other environmental factors could have played a role. Overall, the timing of the decline could be linked to all of these factors and perhaps together, in combination, they were more effective than any one deterrent would have been by itself. The water hyacinth is in remission and this trend could be permanent if control efforts are continued.
Pollution
 Pollution of Lake Victoria is mainly due to discharge of raw sewage into the lake, dumping of domestic and industrial waste, and fertiliser and chemicals from farms.
The Lake Victoria basin, while generally rural, has many major centres of population. Its shores are dotted with key cities and towns, including Kisumu, Kisii, Kenya, Kisii, and Homa Bay in Kenya; Kampala, Jinja, Uganda, Jinja and Entebbe in Uganda; and Bukoba, Mwanza, and Musoma in Tanzania. These cities and towns are also home to many factories that discharge some chemicals directly into the lake or its influent rivers. The set up of small beaches and local authorities around the lake lack proper sewage treatment facilities allowing pollutants to find their way into the water. Large parts of these urban areas also discharge untreated (raw) sewage into the river, increasing its
Pollution of Lake Victoria is mainly due to discharge of raw sewage into the lake, dumping of domestic and industrial waste, and fertiliser and chemicals from farms.
The Lake Victoria basin, while generally rural, has many major centres of population. Its shores are dotted with key cities and towns, including Kisumu, Kisii, Kenya, Kisii, and Homa Bay in Kenya; Kampala, Jinja, Uganda, Jinja and Entebbe in Uganda; and Bukoba, Mwanza, and Musoma in Tanzania. These cities and towns are also home to many factories that discharge some chemicals directly into the lake or its influent rivers. The set up of small beaches and local authorities around the lake lack proper sewage treatment facilities allowing pollutants to find their way into the water. Large parts of these urban areas also discharge untreated (raw) sewage into the river, increasing its eutrophication
Eutrophication is the process by which an entire body of water, or parts of it, becomes progressively enriched with minerals and nutrients, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus. It has also been defined as "nutrient-induced increase in phytopla ...
that in turn is helping to increase the invasive water hyacinth. Increased logging and act of deforestation has led to environmental degradation around the region reducing the absorption of polluting chemicals and deteriorating the water quality.
Environmental data
As of 2016, an environmental data repository exists for Lake Victoria. The repository contains shoreline, bathymetry, pollution, temperature, wind vector, and other important data for both the lake and the wider Basin.History and exploration
 The first recorded information about Lake Victoria comes from Arab traders plying the inland routes in search of gold, ivory, other precious commodities, and slaves.
The first recorded information about Lake Victoria comes from Arab traders plying the inland routes in search of gold, ivory, other precious commodities, and slaves.
 The lake existed and was known to many Africans in the catchment area long before it was sighted by a European ethnic groups, European in 1858 when the British people, British List of explorers, explorer
The lake existed and was known to many Africans in the catchment area long before it was sighted by a European ethnic groups, European in 1858 when the British people, British List of explorers, explorer John Hanning Speke
Captain John Hanning Speke (4 May 1827 – 15 September 1864) was an English explorer and officer in the British Indian Army who made three exploratory expeditions to Africa. He is most associated with the search for the source of the Nil ...
reached its southern shore while on his journey with Richard Francis Burton
Sir Richard Francis Burton (; 19 March 1821 – 20 October 1890) was a British explorer, writer, orientalist scholar,and soldier. He was famed for his travels and explorations in Asia, Africa, and the Americas, as well as his extraordinary kn ...
to explore central Africa and locate the Great Lakes. Believing he had found the source of the Nile on seeing this "vast expanse of open water" for the first time, Speke named the lake after Queen Victoria. Burton, who had been recovering from illness at the time and resting further south on the shores of Lake Tanganyika, was outraged that Speke claimed to have proved his discovery to have been the true source of the Nile River, which Burton regarded as still unsettled. A very public quarrel ensued, which not only sparked a great deal of intense debate within the scientific community of the day, but also much interest by other explorers keen to either confirm or refute Speke's discovery.
In the late 1860s, the famous Scottish explorer and missionary David Livingstone failed in his attempt to verify Speke's discovery, instead pushing too far west and entering the River Congo system instead. Ultimately, the Welsh Americans, Welsh-American explorer Henry Morton Stanley, on an expedition funded by the ''New York Herald'' newspaper, confirmed the truth of Speke's discovery, circumnavigating the lake and reporting the great outflow at Ripon Falls on the lake's northern shore.
Nalubaale Dam
 The only outflow for Lake Victoria is at Jinja, Uganda, where it forms the Victoria Nile. The water for at least 12,000 years has drained across a natural rock weir. In 1952, engineers acting for the government of British Uganda, Colonial Uganda blasted out the weir and reservoir to replace it with an artificial barrage to control the level of the lake and reduce the gradual erosion of the rock weir. A standard for mimicking the old rate of outflow called the "agreed curve" was established, setting the maximum flow rate at 300 to 1,700 Cubic metre per second, cubic metres per second (392–2,224 cubic yard, cu yd/sec) depending on the lake's water level.
In 2002, Uganda completed a second hydroelectric complex in the area, the Kiira Hydroelectric Power Station, with World Bank assistance. By 2006, the water levels in Lake Victoria had reached an 80-year low, and Daniel Kull, an independent hydrologist living in Nairobi, Kenya, calculated that Uganda was releasing about twice as much water as is allowed under the agreement, and was primarily responsible for recent drops in the lake's level.
The only outflow for Lake Victoria is at Jinja, Uganda, where it forms the Victoria Nile. The water for at least 12,000 years has drained across a natural rock weir. In 1952, engineers acting for the government of British Uganda, Colonial Uganda blasted out the weir and reservoir to replace it with an artificial barrage to control the level of the lake and reduce the gradual erosion of the rock weir. A standard for mimicking the old rate of outflow called the "agreed curve" was established, setting the maximum flow rate at 300 to 1,700 Cubic metre per second, cubic metres per second (392–2,224 cubic yard, cu yd/sec) depending on the lake's water level.
In 2002, Uganda completed a second hydroelectric complex in the area, the Kiira Hydroelectric Power Station, with World Bank assistance. By 2006, the water levels in Lake Victoria had reached an 80-year low, and Daniel Kull, an independent hydrologist living in Nairobi, Kenya, calculated that Uganda was releasing about twice as much water as is allowed under the agreement, and was primarily responsible for recent drops in the lake's level.
Water use
Many towns and cities are reliant on Victoria for their water supplies, for farming and other uses.Lamadi water scheme
The Lamadi water scheme is a water and sanitation project that serves Mwanza and the satellite towns of Lamadi, Misungwi, Magu, Bukoba, and Musoma on the bank of Lake Victoria. European Investment Bank started the project in 2013 with the aim of protecting the environmental health of the lake, through improved water and sanitation to the towns whose pollution is part of the degradation of the lake. The project aims to provide safe drinking water for an estimated one million people and improved sanitation for 100 000 people. Sediment and suspended solids are filtered out using sand, which acts like a sieve. The water is then ready to be chlorinated or treated in another way. The sand filtration helps reduce water-borne diseases and is based on the use of the local environment.Transport
Since the 1900s, Lake Victoria ferries have been an important means of transport between Uganda, Tanzania, and Kenya. The main ports on the lake are Kisumu, Mwanza, Bukoba,Entebbe
Entebbe is a city in Central Uganda. Located on a Lake Victoria peninsula, approximately southwest of the Ugandan capital city, Kampala. Entebbe was once the seat of government for the Protectorate of Uganda prior to independence, in 1962. T ...
, Port Bell, and Jinja. Until 1963, the fastest and newest ferry, MV Victoria (1959), MV ''Victoria'', was designated a Royal Mail Ship. In 1966, train ferry services between Kenya and Tanzania were established with the introduction of and . The ferry MV Bukoba, MV ''Bukoba'' sank in the lake on 21 May 1996 with a loss of between 800 and 1,000 lives, making it one of Africa's worst maritime disasters. Another tragedy occurred recently on 20 September 2018 that involved the passagers ferry Sinking of MV Nyerere, MV Nyerere from Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
that caused the deaths of over 200 people.
On 6 November 2022, Lake Victoria was the site of a commercial passenger aircraft crash. Precision Air Flight 494 an ATR 42, ATR 42–500 carrying 39 passengers and four crew, crashed while approaching Bukoba Airport, resulting in 19 fatalities.
See also
* ''Darwin's Nightmare'' * KishandaReferences
External links
Decreasing levels of Lake Victoria Worry East African Countries
New Scientist article
on Uganda's violation of the agreed curve for hydroelectric water flow.
Dams Draining Lake Victoria
''A Naturalist on Lake Victoria, with an Account of Sleeping Sickness and the Tse-tse Fly''
(1920). T.F. Unwin Ltd, London; Biodiversity Archive
Video of Lake Victoria
* Institutions of the East African Community
Lake Victoria Fisheries Organisation
{{DEFAULTSORT:Victoria Lake Victoria, African Great Lakes Lakes of Kenya Lakes of Tanzania Lakes of Uganda Geography of Kampala Nile Kenya–Uganda border Kenya–Tanzania border Tanzania–Uganda border International lakes of Africa Border tripoints Geography of Kagera Region Geography of Mwanza Region Geography of Mara Region Kisumu County Homa Bay County